Both the Tru-Seq and NEB libraries were amplified pre-hybrid capture – another step at which modifications were made, according to how much DNA there was in each library. Bioanalyser traces for the pre-amplification Tru-Seq libraries are shown below:
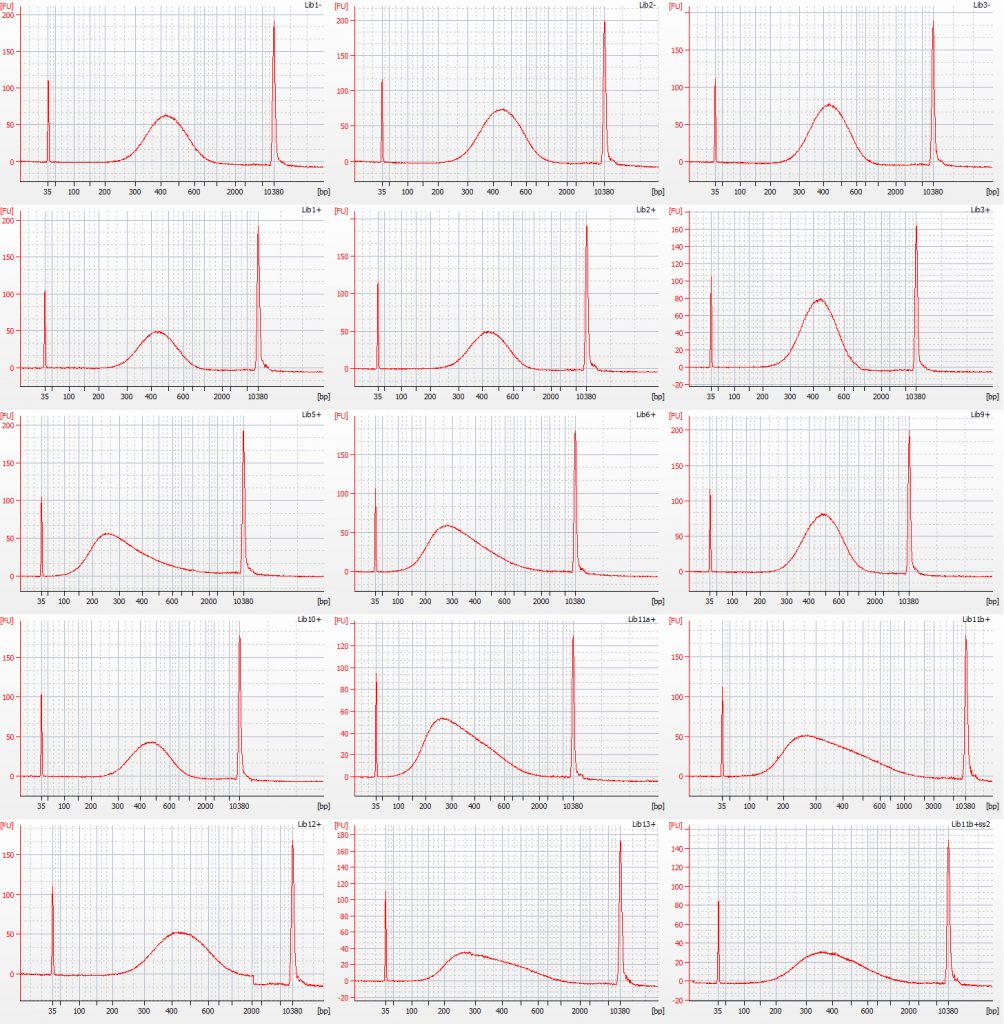
Bioanalyser traces for size selected Inga umbellifera Tru-Seq libraries: unrepaired DNA: 2009 herbarium; 2009 silica; 2009 silica; repaired DNA: 2009 herbarium, 2009 silica, 2009 herbarium, 1948; 1948; 2004 herbarium; 2004 herbarium; 1932 flower; 1932 flower; 1932 leaf; 1985; 1932 flower size select 2
The number of PCR amplification cycles used for both Tru-Seq and NEB for each library are given in the last two columns of the following table:
| Year | Sample |
DNA repair | Sonic cycles | Post-sonic cleanup | Size Select | TruSeq ng | NEB ng | Library No. | Tru-Seq amp cycles | NEB amp cycles |
| 2009 | H-L | – | 8 | yes | normal | 101 | 100 | 1- | 8 | 7 |
| 2009 | H-L | + | 8 | yes | normal | 101 | 101.5 | 1+ | 8 | 7 |
| 2009 | H-L | – | 8 | yes | normal | 101 | 100 | 2- | 8 | 7 |
| 2009 | H-L | + | 8 | yes | normal | 70.6 | 28.2 | 2+ | 9 | 10 |
| 2009 | S-L | – | 8 | yes | normal | 101 | 100 | 3- | 8 | 7 |
| 2009 | S-L | + | 8 | yes | normal | 101 | 94 | 3+ | 8 | 7 |
| 2004 | H-L | + | 3 | yes | normal | 101 | 100 | 9+ | 8 | 7 |
| 2004 | H-L | + | 3 | yes | normal | 70.6 | 39.1 | 10+ | 9 | 10 |
| 1948 | H-L | + | — | — | modified | 70 | 22.9 | 5+ | 8 | 10 |
| 1948 | H-L | + | — | — | modified | 80 | 58.8 | 6+ | 8 | 7 |
| 1932 | H-F | + | — | — | modified | 80 | 80 | 11+a | 8 | 8 |
| 1932 | H-F | + | — | — | modified | 80 | 80 | 11+b | 8 | 8 |
| 1932 | H-F | + | — | — | modified | 40 | — | 11+b2 | 8 | — |
| 1932 | H-F | + | — | — | — | — | 40 | 11+bv2 | — | 10 |
| 1932 | H-L | + | 3 | yes | normal | 101 | 100 | 12+ | 8 | 7 |
| 1840 | H-L | + | — | — | — | — | 5 | 8+ | — | 12 |
| 1840 | H-L | + | — | — | — | — | very low | 7+ | — | 12 |
| 1835 | H-L | + | 1 | no | modified | 40.4 | 16 | 13+ | 10 | 10 |
Bioanalyser traces for the post-amplification Tru-Seq libraries are shown below:
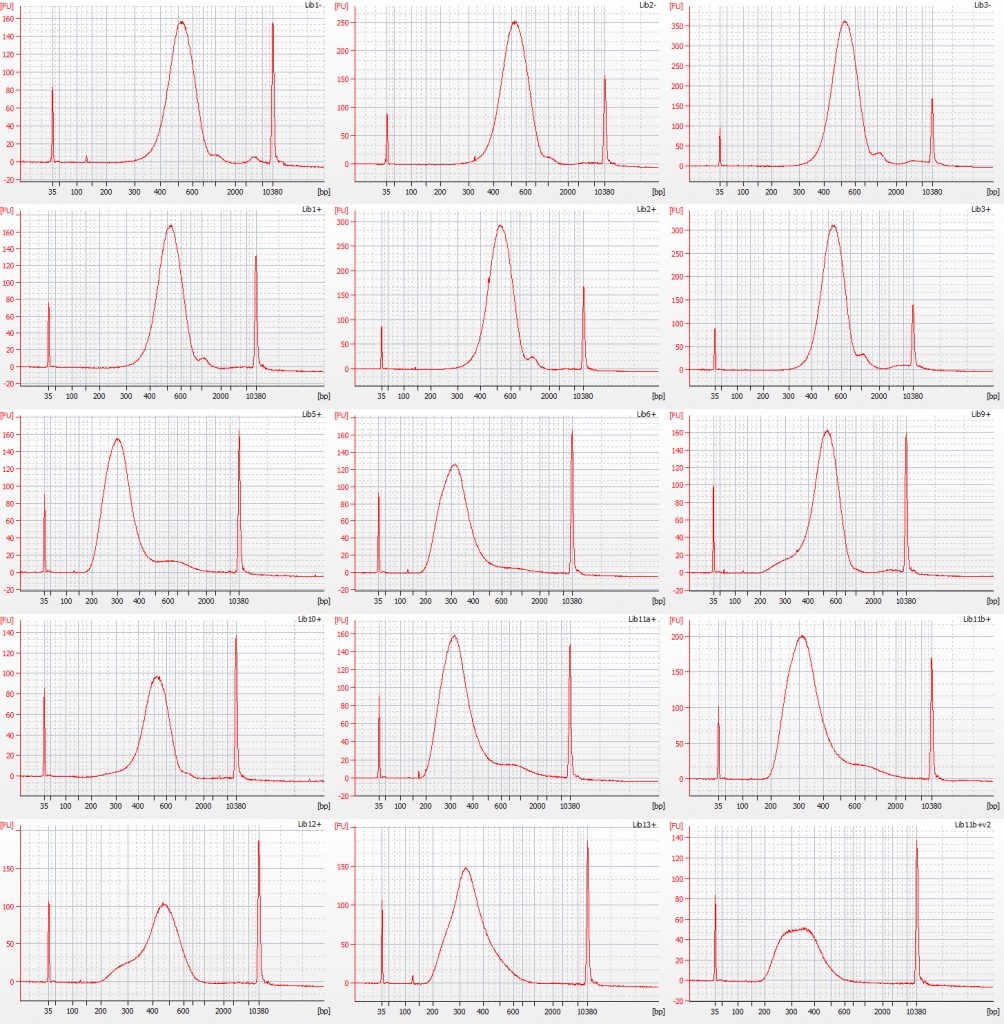
Bioanalyser traces for amplified Inga umbellifera Tru-Seq libraries: top row – unrepaired DNA: 2009 herbarium; 2009 silica; 2009 silica; repaired DNA: second row – 2009 herbarium, 2009 silica, 2009 herbarium; third row – 1948; 1948; 2004 herbarium; fourth row – 2004 herbarium; 1932 flower; 1932 flower; bottom row – 1932 leaf; 1835; 1932 flower size select 2
The peaks of the amplified TruSeq libraries are far higher, although the first six libraries also show a small peak at around 2x the main peak size. It is possible that this is a product of slight over-amplification of the libraries. Initially we wondered if it could have been due to a small carry-over of beads, but replacing the tubes on the magnet and repipetting the sample off did not remove or reduce this peak. There is also a small adaptor peak visible in some of the traces at c. 120 bp.
For the NEB libraries, we did not generate BioAnalyser traces pre-amplification. The post-amplification NEB Bioanalyser traces are shown below, for comparison with the Tru-Seq traces above:
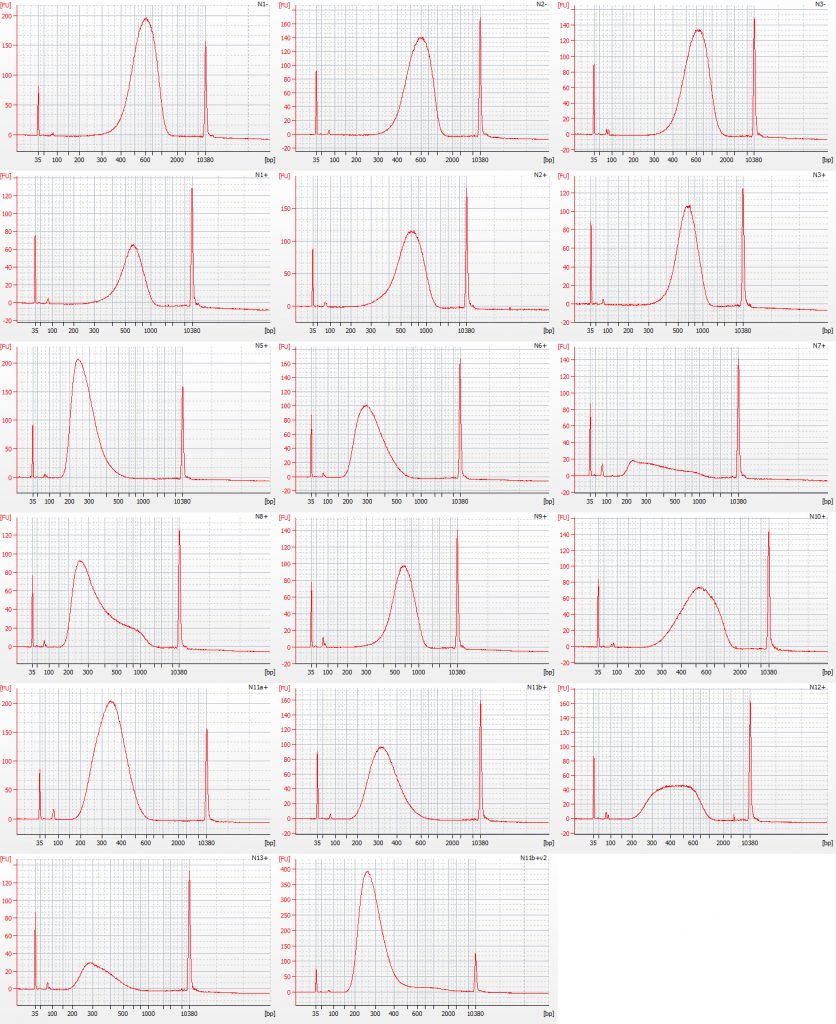
Bioanalyser traces for size selected Inga umbellifera NEB libraries: top row – unrepaired DNA: 2009 herbarium; 2009 silica; 2009 silica; repaired DNA: second row – 2009 herbarium, 2009 silica, 2009 herbarium; third row – 1948; 1948; 1840; fourth row – 1840; 2004; 2004; fifth row – 1932 flower; 1932 flower; 1932 leaf; bottom row – 1835; 1932 flower size select 2
A small adaptor peak is visible at c. 60 bp. One 1840 library (final sample on row three) was generated from far less than the minimum recommendation of 5 ng of repaired DNA for the NEB protocol we were following; the other 1840 library (first sample on row four) was generated from 5 ng of repaired DNA, and clearly has a far better DNA fragment size distribution.
We then sorted all 32 Tru-Seq and NEB post-amplification libraries into three pools of libraries with compatible adaptor sequences, taking into account average library fragment size, for three separate hybrid capture reactions.
Pool 1: 439-472 bp: no DNA repair: Tru-Seq and NEB, 2009 herbarium and 2009 silica; DNA repair: Tru-Seq and NEB, 2009 herbarium and 2009 silica.
Pool 2: 450-520 bp: no DNA repair: Tru-Seq and NEB, 2009 herbarium; DNA repair: Tru-Seq and NEB, 2004 herbarium, 1932 leaf; Tru-Seq, 1932 flower (size select 2).
Pool 3: 350-400 bp: DNA repair: TruSeq and NEB, 1948, 1932 flower, 1835; NEB, 1840, 1932 flower (no size select).
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. I. What it’s all about. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/16411
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. II. Inga. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/16427
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. III. The samples. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/16441
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. IV. DNA. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/16470
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. V. Fragmenting the DNA. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/16525
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. VI. Size Selection. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/16645
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. VII. Comparisons. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/16737
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. VIII. Amplification. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/16788
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. IX. Hybrid capture. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/17298
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. X. An update. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/20751
Capturing Genes from Herbaria. XI. Some metagenomics of a herbarium specimen. http://stories.rbge.org.uk/archives/20817
